A partnership between Google Australia, Queensland University of Technology, and the Australian Acoustics Observatory, A2O is an innovative acoustic search engine powered by Google AI. Designed to revolutionize how we analyze and understand ecosystem sounds, this advanced platform harnesses millions of hours of audio, providing unprecedented insights into wildlife and their habitats.

Wildlife sounds are crucial to understanding the presence of certain species, their movements, interspecies relationships, and migratory patterns. Sounds play a huge role in wildlife conservation because they can be recorded passively across different locations without seeing the animals. Combined with location and time metadata, audio is a powerful fingerprint of wildlife.
Over the last few months, we have worked on building an audio search platform powered by Google AI and millions of hours of audio recordings from the Australian Acoustics Observatory.
Alongside these partners and the Queensland University of Technology, we are excited to share A2O Search, available now: search.acousticobservatory.org.
Audio Similarity Search
Audio is a powerful fingerprint for wildlife.
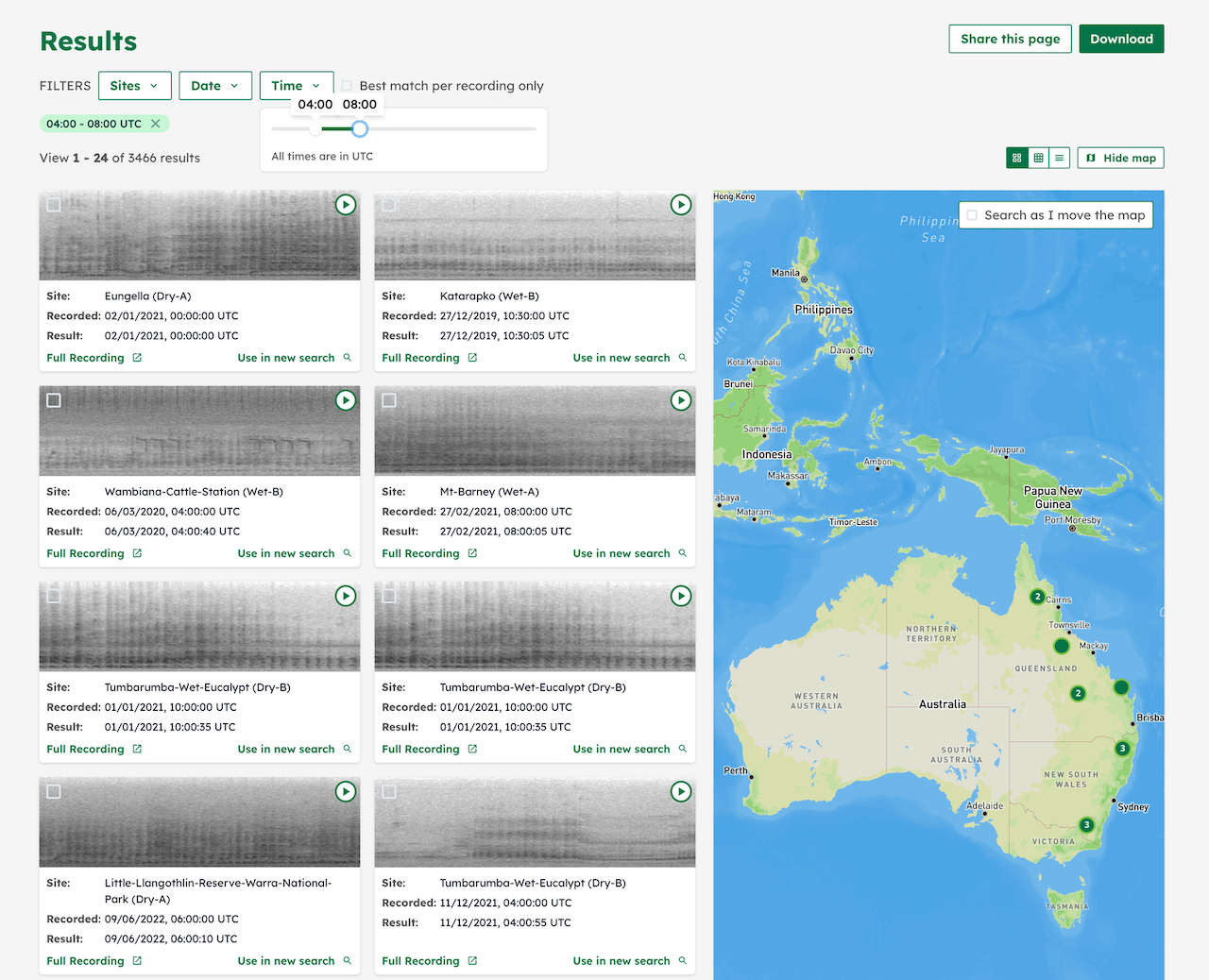
Looking at distribution of search results based on geography and time of day
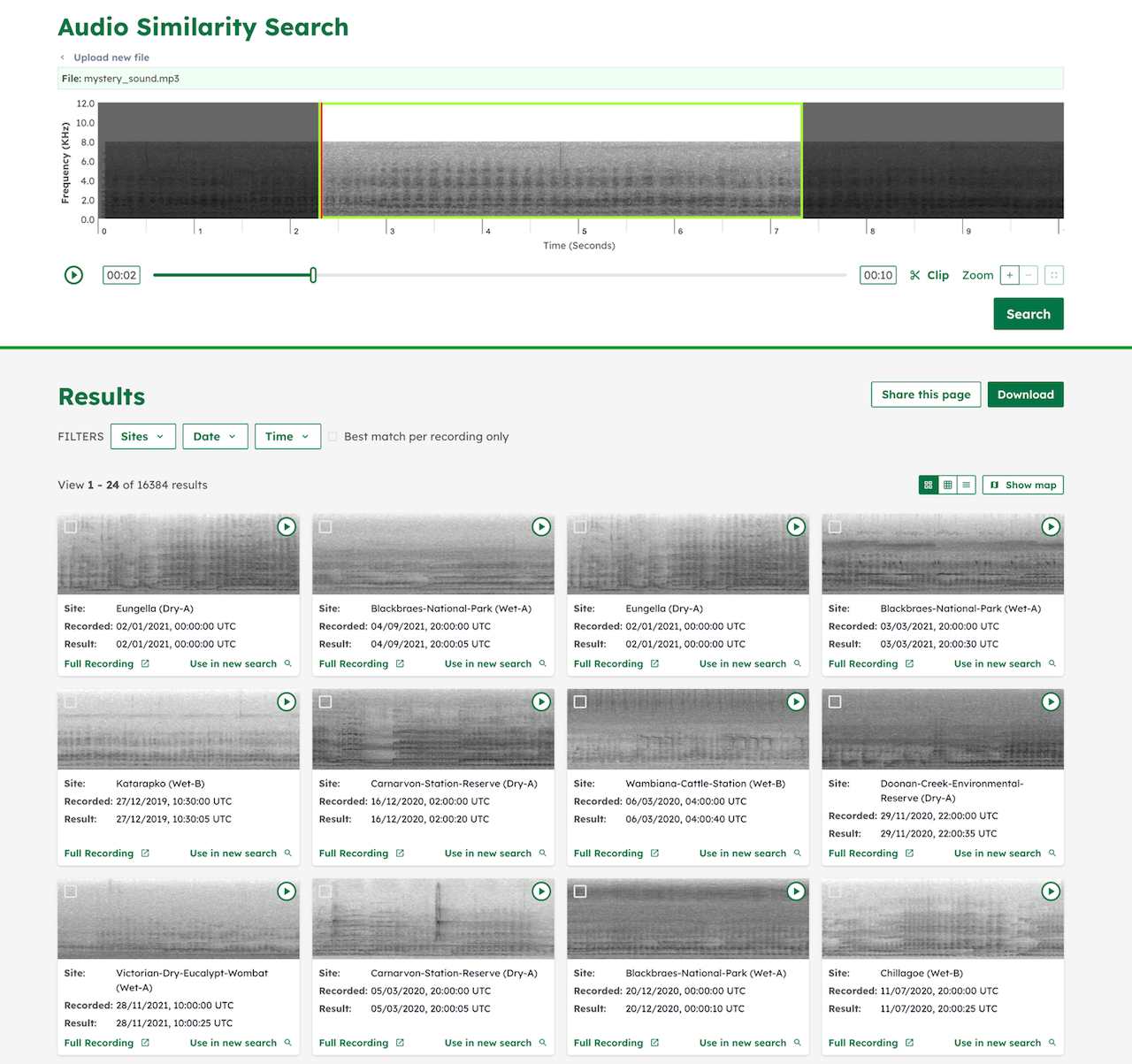
Recording audio is only part of the puzzle. Analyzing the sounds is a long and laborious process. Traditional approaches require researchers to listen to the audio clips manually, sifting through hours of recordings to distinguish animal sounds from background noise and then identify the exact species. With the recent audio recognition developments at Google AI, we can reduce this time-consuming process by filtering out parts of the audio clip with background noise, and perform searches on the relevant portions to find the presence of various species in the audio repository. These similarity search results can then be extended to understand different patterns — Where did these recordings come from? What time of day? What were the other sounds around the same time?
This type of search can be conducted quickly across an extensive archive, and allows us to derive deep insights into behavioral and population patterns in our heavily changing ecosystems. Another major benefit of audio similarity search is that it enables fast annotation of existing audio archives. With A2O Search, you can identify all matching recordings and quickly label the data for further fine-tuning of machine learning models.
Looking at distribution of search results based on geography and time of day
Scalable Infrastructure on Google Cloud
A2O Search allows researchers to upload an audio clip or record from their phone, and search for similar sounds in the A2O audio collection. A spectrogram of the uploaded audio is generated on the client-side to enable fast visual assessment and precise clipping.
We chose Milvus as our vector database because of our familiarity working with FAISS, its scalability and various index management features. The search API is built using Django and all the infrastructure components are orchestrated using Kubernetes.
Looking Ahead
The search API and components are built to be open sourced, and we believe this project can be scaled to similar audio recognition use cases with relatively low investment. If you have an idea of how similarity search could help you gain insights into your data, please reach out, I'd love to talk.
What we're doing.
Latest